In 2025, customer data represents one of the most valuable assets any business possesses. CRM systems hold the keys to understanding customer behavior, predicting future needs, optimizing sales processes, and delivering personalized experiences. Yet most organizations face an uncomfortable truth: their CRM databases are drowning in poor-quality data.
Research reveals that CRM data decays at approximately 34% annually. Nearly half of all companies estimate losing more than 10% of annual revenue due to poor data quality. Contact information becomes outdated through job changes, email addresses get abandoned, company names shift through mergers and acquisitions, and duplicate records multiply as data flows in from countless sources.
For years, businesses fought this battle through periodic manual cleanups—dedicating teams to merge duplicates, update outdated information, and standardize formats. This approach has always been labor-intensive, expensive, and ultimately futile. By the time cleanup finishes, new dirty data has already accumulated.
The future lies in self-cleaning systems that use AI, machine learning, and automation to maintain data hygiene continuously and autonomously. These platforms prevent problems before they occur, automatically correct errors when detected, and continuously improve accuracy over time.
This article explores how self-cleaning systems work, highlights leading platforms, discusses the critical role of migration and integration, and provides actionable best practices for transforming your approach to data quality.
The High Cost of Poor CRM Data Quality

Poor data quality devastates business operations far beyond mere inconvenience—it directly undermines growth, wastes resources, and damages customer relationships.
Revenue Loss and Missed Opportunities
Sales teams waste 17-23% of their time on data entry and administrative tasks rather than selling. When that data proves inaccurate, this investment yields zero return. Representatives pursue dead leads, contact people who've changed jobs, and reach out to invalid email addresses and phone numbers.
Research shows 45% of sales leaders lack confidence in forecasting accuracy specifically due to poor data quality. When pipeline data can't be trusted, strategic planning becomes guesswork. Companies lose an estimated 10%+ of annual revenue to data quality issues—$1 million or more for a $10 million business.
Wasted Marketing Investment
Every email to a dead address wastes budget and damages sender reputation. With B2B data decaying at 22% annually, significant marketing spend evaporates targeting non-existent prospects. Poor data undermines personalization efforts—when customer preferences, purchase history, and needs aren't accurately captured, engagement plummets and lifetime value suffers.
Marketing automation becomes a liability when fed bad data, sending wrong messages to wrong people at massive scale, damaging brand reputation faster than manual processes ever could.
Compromised Decision-Making
Executives rely on CRM data for strategic decisions: resource allocation, market entry, product development, territory planning. When foundational data is inaccurate or incomplete, these decisions rest on flawed assumptions. Duplicate records skew customer counts, incomplete records hide patterns, inconsistent formatting makes analysis unreliable.
Leadership operates partially blind, making decisions with false confidence about business landscape understanding.
Degraded Customer Experience
Customers expect businesses to remember preferences, understand needs, and provide seamless experiences. Support representatives can't resolve issues quickly when interaction history is scattered across duplicate records. Sales outreach feels impersonal when purchase history is incomplete.
Poor data quality makes every interaction harder, slower, and less satisfying—driving customers to competitors demonstrating better understanding.
Operational Inefficiency and Compliance Risks
Teams waste hours searching for correct information, reconciling conflicting records, and manually correcting errors. Integration between systems breaks down when data quality varies. Automated workflows fail when encountering unexpected formats or missing fields.
Data privacy regulations like GDPR require accurate customer data and ability to honor deletion requests. Poor quality makes compliance exponentially harder—how do you delete all records for a customer if duplicates are scattered under different names?
Understanding CRM Data Decay
Data quality deteriorates through multiple mechanisms. Understanding these helps combat them effectively.
Natural Data Obsolescence
Job Changes: Professionals change employers frequently. When contacts switch jobs, email addresses, phone numbers, company affiliations, and titles become inaccurate simultaneously. Approximately 20-30% of B2B contact data becomes obsolete annually through job changes alone.
Company Evolution: Businesses merge, rebrand, relocate, change phone numbers, update websites, and shut down. Even thriving companies reorganize, creating new departments and shifting responsibilities, rendering organizational data inaccurate.
Life Events: For B2C, marriages, divorces, relocations, births, and retirements change names, addresses, household composition, and needs.
Human Error in Data Entry
Manual entry introduces errors constantly:
- Typos and misspellings ("John" becomes "Jonh")
- Inconsistent formatting (phone numbers as "(555) 123-4567" vs "5551234567")
- Incomplete information when users rush through required fields
- Copy-paste errors from business cards or websites
- Placeholder data ("TBD", "unknown") that never gets corrected
System Integration Issues
Mapping Errors: Incorrect field mappings cause data to flow into wrong destinations or get truncated.
Sync Conflicts: When records exist in multiple systems and update in different places, inconsistencies emerge without clear authority.
Data Transformation: Date formats scramble across regional settings, currency conversions use outdated rates, special characters corrupt during encoding changes.
Import Failures: Bulk imports from spreadsheets, purchased lists, or events include formatting inconsistencies that slip past validation.
Duplicate Record Creation
Multiple Entry Points: Web forms, email, phone, social media, events, and partner channels each might create new records rather than updating existing ones.
Variation in Identifying Information: "Bob Smith" vs "Robert Smith" or different email addresses for different purposes get treated as separate individuals without sophisticated matching.
Lack of Deduplication: Without automated processes running regularly, small duplicate creation rates compound into major problems.
The Compounding Problem
Data decay is continuous and accelerating. A 95% accurate database today becomes 92% accurate in six months and 88% accurate in a year—even with no new data entry—through natural obsolescence alone. Add human error and integration issues, and decay accelerates further.
This makes periodic manual cleanups inadequate. The only sustainable approach matches continuous decay with continuous automated quality management.
What Are Self-Cleaning CRM Systems

Self-cleaning systems represent the next evolution in customer data management, using AI, machine learning, and automation to maintain hygiene continuously and autonomously.
Core Characteristics
Continuous Monitoring: Systems don't wait for scheduled maintenance. They continuously scan records, identifying quality issues as they occur or before they materialize.
Automated Correction: When issues are detected, systems automatically apply fixes based on learned patterns, predefined rules, and confidence thresholds. Simple, high-confidence corrections happen instantly. Complex issues get flagged for human review.
Preventative Validation: Rather than just cleaning data after entry, platforms implement validation at point of entry. Invalid formats get caught immediately, preventing dirty data from entering.
Intelligent Learning: Systems improve over time, learning from corrections, user behavior, and outcomes. Machine learning models initially struggle with certain duplicates but become progressively better.
Multi-Dimensional Approach: Self-cleaning addresses the full spectrum simultaneously—deduplication, standardization, validation, enrichment, and obsolescence detection—rather than tackling problems in isolation.
How They Differ from Traditional Approaches
Traditional management follows a reactive, periodic model:
- Data accumulates and quality degrades
- Problems become visible
- Cleanup project initiates
- Resources dedicate to manual review
- Quality improves temporarily
- Cycle repeats
This is expensive, disruptive, incomplete, and temporary.
Self-cleaning follows a proactive, continuous model:
- Data enters through validated entry points
- Automated processes continuously monitor
- Problems detect and correct in real-time
- Machine learning improves over time
- Quality remains consistently high
- Resources freed for strategic work
Benefits
- Sustained Quality: Consistent quality over time rather than saw-tooth patterns
- Resource Efficiency: 60%+ reduction in manual data quality work
- Faster Time-to-Value: New data immediately useful
- Improved Trust: When users trust data accuracy, adoption increases
- Scalability: Handles enterprise-level volumes automatically
- Continuous Improvement: Gets progressively better with use
How AI-Powered Data Cleansing Works
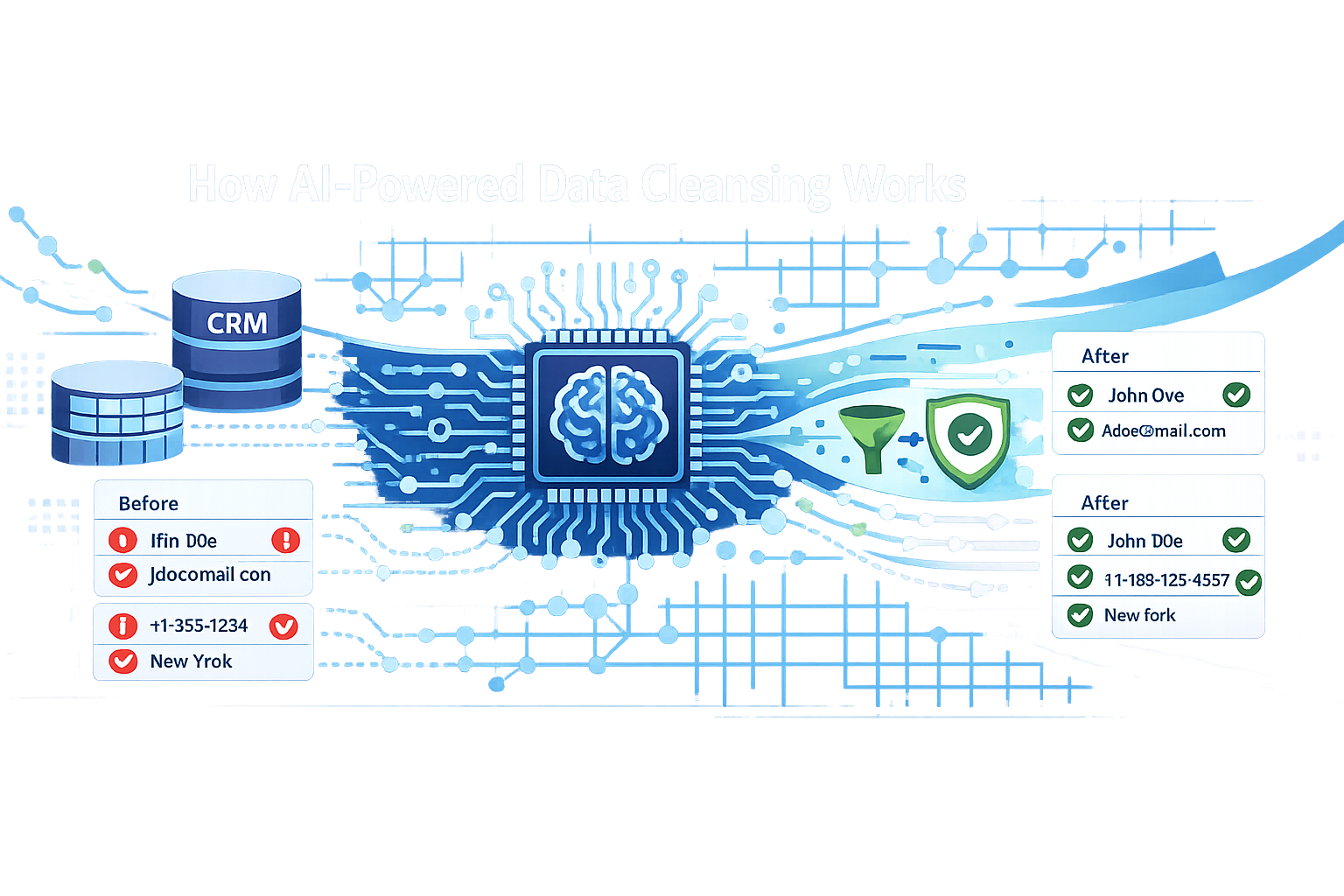
Modern self-cleaning operates through coordinated processes:
1. Data Profiling and Assessment
Systems scan entire databases to understand what exists:
Completeness Analysis: Calculate percentages of records with data vs empty fields, revealing patterns and prioritizing enrichment.
Format Consistency: Identify variations—phone numbers in fifteen formats, company names in dozens of variations.
Validity Assessment: Check email formats and deliverability, verify phone numbers against known patterns, validate addresses against postal databases.
Duplicate Detection: Identify potential clusters based on exact matches, similar names with same company, and fuzzy matching across multiple fields.
Anomaly Identification: Flag records deviating from expected patterns—impossible ages, suspicious deal values, email addresses at questionable domains.
2. Automated Standardization
Format Normalization: Convert phone numbers to consistent format, standardize company names to canonical forms, format addresses according to postal standards.
Case Correction: Properly capitalize names, lowercase email addresses, standardize state and country codes.
Data Type Enforcement: Ensure numeric fields contain numbers, standardize dates, normalize boolean fields.
Whitespace Cleanup: Remove leading/trailing spaces, collapse multiple spaces to singles.
3. Intelligent Deduplication
Multi-Field Matching: Examine multiple fields with different weights. Exact email match might be definitive; similar name plus same company plus similar title indicates probable duplication.
Fuzzy Logic: Recognize "Robert" and "Bob" as likely same person, "Acme Corp" and "Acme Corporation" as same company.
Relationship Context: Consider relationships—two similar names at same company more likely duplicates than similar names at different companies.
Confidence Scoring: High-confidence matches auto-merge, medium-confidence flagged for review, low-confidence logged but not acted upon.
Intelligent Merging: Decide which data to keep—typically most recent, but configured based on business logic.
4. Data Validation and Verification
Email Verification: Check deliverability without sending messages, catching typos and abandoned addresses.
Phone Number Validation: Verify against valid patterns for country codes, check if currently active.
Address Verification: Confirm addresses are valid, deliverable locations using postal databases.
Company Data Validation: Verify names, addresses, employee counts against business intelligence platforms.
Cross-Field Consistency: Check logical consistency—if country is "USA" but state is Canadian province, flag error.
5. Automated Enrichment
Publicly Available Information: Scrape LinkedIn, company websites, social media, business directories for missing details.
Third-Party Data Sources: Integrate with commercial providers for firmographic, demographic, and intent data.
Relationship Inference: Connect contacts to companies, link contacts sharing email domains, identify organizational hierarchies.
Activity-Based Enrichment: Capture website visits, email opens, content downloads, support tickets, purchases without manual entry.
6. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Pattern Learning: Analyze which records tend to be accurate vs error-prone, flagging high-risk records for frequent validation.
Feedback Loops: Learn from manual corrections, adjusting algorithms when users regularly merge records the system didn't automatically identify.
Anomaly Detection Refinement: As systems process more data, understanding of normal vs anomalous improves.
7. Prevention at Point of Entry
Real-Time Validation: Web forms and data entry interfaces validate inputs before accepting them.
Dropdown Standardization: Replace free-text with controlled vocabularies where possible.
Duplicate Prevention: Check whether matching records exist before creating new ones.
Smart Defaults: Pre-populate fields based on context—if email domain matches known company, auto-fill company data.
Prevention is always more efficient than remediation.
Key Components of Modern Data Quality Systems
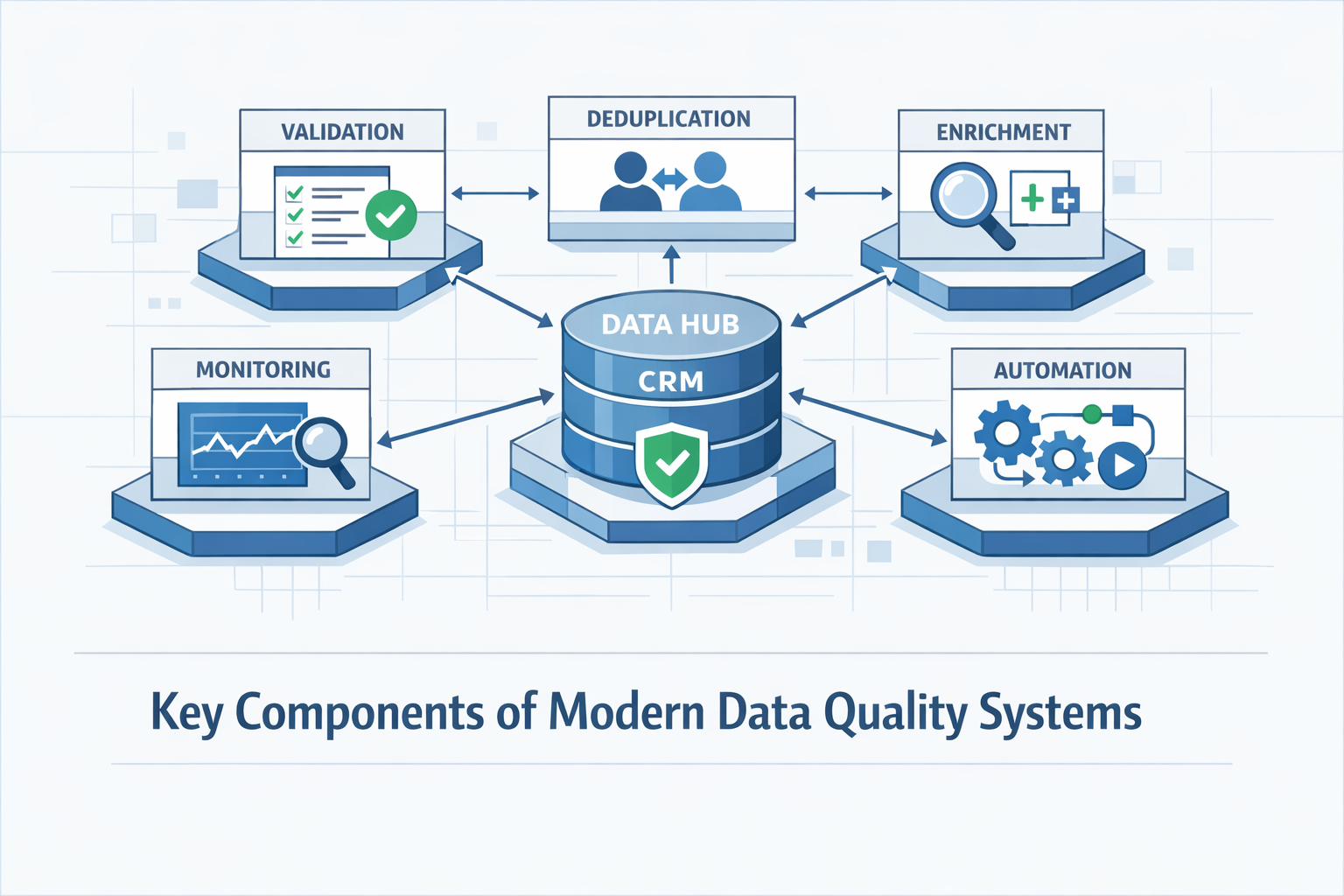
Comprehensive quality management requires multiple coordinated components:
Deduplication Engines
- Advanced fuzzy matching algorithms
- Confidence scoring for automated vs manual merging
- Merge logic determining which data to preserve
- Complete audit trails of merge operations
- Ongoing monitoring beyond one-time cleanup
Validation and Verification Services
- Real-time email validation and deliverability checking
- Phone number verification for format and active status
- Address standardization via postal databases
- Data type enforcement ensuring appropriate content
Data Enrichment Integrations
- Third-party business intelligence platforms
- Web scraping of publicly available information
- Intent data from monitoring services
- Social media integration for profiles and engagement
Automated Standardization
- Configurable format rules for each field type
- Controlled vocabularies for categorical fields
- Data normalization to canonical forms
Rule Engines and Workflow Automation
- Business logic implementation for data quality requirements
- Automated routing of issues requiring human review
- Clear exception handling processes
Machine Learning and AI
- Predictive data quality scoring
- Anomaly detection
- Continuous learning from corrections and outcomes
Monitoring and Reporting
- Real-time dashboards showing key metrics
- Trend analysis revealing patterns
- Automated alerting when metrics fall below thresholds
Integration Frameworks
- API connectivity across technology stack
- Bidirectional synchronization
- Conflict resolution logic
Leading CRM Platforms with Self-Cleaning Capabilities

Major CRM vendors integrate increasingly sophisticated self-cleaning capabilities:
Salesforce with Einstein Data Detect
Salesforce has invested heavily in AI-powered data quality through Einstein platform.
Key Capabilities:
- Intelligent Duplicate Detection: Einstein uses fuzzy matching and machine learning to identify duplicates even when data doesn't match exactly, learning from user merge decisions
- Automated Activity Capture: Automatically logs emails and calendar events from Gmail and Outlook, ensuring complete activity records
- Field Recommendations: Analyzes patterns in how users complete records, suggesting most valuable fields for specific record types
- Data Quality Dashboards: Built-in reporting providing visibility into duplicate rates, completeness metrics, and trends
- Integration Ecosystem: AppExchange includes numerous data quality applications from partners like RingLead, DemandTools, and Validity
For organizations invested in Salesforce ecosystem, these integrated capabilities provide powerful quality management without additional platforms.
monday.com CRM with AI-Powered Automation
monday.com emphasizes user-friendly automation and intelligent data management without technical expertise requirements.
Key Capabilities:
- No-Code Automation: Create sophisticated data quality automations through visual workflows without coding
- AI-Powered Suggestions: Platform analyzes usage patterns and suggests automations to improve quality based on team behavior
- Smart Data Extraction: AI automatically extracts structured data from emails and documents, populating fields without manual entry
- Collaborative Data Management: Visual, collaborative interface makes it easy for teams to participate in quality initiatives
- Integration Hub: Connections to enrichment services, validation tools, and other platforms enable ecosystem-wide quality
monday.com excels at making advanced capabilities accessible to non-technical teams, ideal for organizations valuing simplicity and rapid implementation.
Pipedrive with Smart Contact Data
Pipedrive focuses quality capabilities specifically on sales team productivity.
Key Capabilities:
- Smart Contact Data: Automatically enriches contact and company records with publicly available information
- Duplicate Detection: Identifies potential duplicate contacts and organizations, prompting merging
- Email Integration and Auto-Logging: Bidirectional sync ensures communications automatically log
- Mobile Data Capture: Apps make it easy to capture information on the go, preventing information loss
- Workflow Automation: Configure workflows to validate completeness, flag missing information, trigger enrichment at appropriate stages
- LeadBooster Add-On: Chatbot, web forms, and prospector tools capture high-quality lead data at first contact
For small to mid-sized sales organizations, Pipedrive provides practical capabilities that integrate naturally into daily workflows.
Zoho CRM with Zia AI
Zoho offers comprehensive data quality capabilities through Zia AI at accessible price points.
Key Capabilities:
- Zia Data Enrichment: Automatically appends missing information using publicly available data sources
- Duplicate Detection and Management: Identifies potential duplicates across modules, auto-merging based on configurable rules
- Data Validation Rules: Comprehensive framework for required fields, acceptable ranges, dependencies, custom logic
- Anomaly Detection: Machine learning identifies unusual patterns indicating potential quality issues
- Workflow Automation: Trigger workflows based on quality conditions—alerts for missing fields, cleanup task assignment
- Integration with Zoho Ecosystem: Quality processes integrate seamlessly across Zoho's business application suite
For organizations seeking enterprise-grade capabilities without enterprise pricing, Zoho provides exceptional value.
The Critical Role of Data Migration
No amount of self-cleaning can fully remediate poor-quality data inherited from legacy systems. Migration represents both challenge and opportunity.
Migration as Data Quality Opportunity
Clean Slate Potential: Migration enables starting fresh with only validated, deduplicated, current data rather than perpetuating accumulated errors.
Forced Data Audit: Migration requires examining what exists, how it's structured, what needs preserving—often revealing significant portions add no value.
Structure Optimization: New platforms might offer better data models, more appropriate field types, improved relationship structures.
Standardization Enforcement: During migration, data can be standardized to canonical formats regardless of source system variations.
Enrichment Opportunity: Migration is ideal for enriching records with missing information from external sources.
The Migration Challenge
Garbage In, Garbage Out: Simply moving existing data without cleaning propagates all problems into new systems.
Complexity and Data Loss Risks: CRM databases contain complex relationships requiring sophisticated processes to preserve while cleaning and transforming.
Downtime and Business Disruption: Migration can disrupt operations if not executed carefully while teams need continuous customer data access.
Resource Intensity: Effective migration requires significant investment in planning, execution, validation, and post-migration reconciliation.
Solutions from MigrateMyCRM
MigrateMyCRM (formerly Trujay) specializes in making CRM migration secure, accurate, and efficient while establishing exceptional data quality in new systems. With over 4,270 successful migrations completed, their platform combines automation, intelligence, and expertise.
Comprehensive Platform Capabilities
Broad Platform Support: Supports migration between 25+ cloud-based CRM systems plus CSV and Excel files, with 50+ additional connectors for custom scenarios.
AI-Powered Automapping: Rather than manual field-by-field mapping, intelligent automapping analyzes source and destination systems, automatically identifying corresponding fields, objects, and relationships, dramatically reducing setup time while improving accuracy.
Unlimited Free Sample Migrations: Run sample migrations with approximately 10% of data at no cost, enabling thorough testing, validation, issue identification, and process refinement before full execution. Iterate until perfect without risk.
Advanced Duplicate Prevention: Sophisticated matching logic identifies potential duplicates based on configurable criteria—company name and domain, email addresses, names and phone numbers, custom field combinations. Choose to merge during migration or preserve for manual review.
Custom Field Management: Bulk create custom fields directly from migration interface, dramatically accelerating configuration and ensuring no custom data loss.
Complete Relationship Preservation: All relationships between records maintain—contacts linked to companies, opportunities connected to contacts and accounts, activities associated with opportunities. Even complex multi-level relationships in custom objects preserve.
Field Usage Analytics: Before migration, analyze which fields actually contain data and usage frequency, enabling informed decisions about what to migrate versus archive.
Data Transformation During Migration: Transform data during migration—standardize formats, split fields, combine data, apply calculations, map picklist values to new standards.
Enterprise-Grade Security: ISO certified and GDPR compliant, trusted by organizations with strictest security requirements. All transmission encrypted, access tightly controlled, comprehensive audit trails document every operation.
Migration Process Options
Self-Service: Organizations with technical resources execute migrations independently using intuitive interface, comprehensive documentation, built-in validation.
Guided Assistance: For complex scenarios, migration specialists provide expert guidance while organizations maintain control—help with planning, mapping validation, issue resolution, best practices.
Full-Service: Engage MigrateMyCRM team to handle entire migration from initial audit through final validation, ideal for complex migrations or resource-constrained teams.
Migration Best Practices
Based on thousands of successful migrations, MigrateMyCRM recommends:
- Start with Data Audit: Thoroughly audit source quality before beginning—identify duplicates, assess completeness, validate accuracy
- Clean Before Migration: Use migration as opportunity to deduplicate, standardize, enrich
- Leverage Sample Migrations: Run multiple samples, validate thoroughly, refine until perfect
- Plan for Post-Migration Validation: Have clear success criteria and validation processes
- Communicate with Stakeholders: Keep teams informed about timeline, impacts, validation roles
- Schedule Strategically: Execute during low-activity periods—weekends, holidays, fiscal transitions
Migration as Quality Foundation
When executed thoughtfully with expert support, migration establishes high-quality foundations that self-cleaning systems maintain:
- Duplicates eliminated, preventing compound growth
- Standards established, providing baselines for variation detection
- Completeness improved, reducing enrichment burden
- Confidence restored in teams that lost trust in CRM quality
Organizations viewing migration as strategic data quality initiative create competitive advantages compounding over years.
CRM Integration and Data Quality

Self-cleaning maintains quality within CRM platforms, but most organizations operate complex ecosystems where customer data flows across multiple systems. Integration quality directly impacts overall data quality.
Why Integration Matters for Data Quality
Modern businesses typically operate:
- CRM Systems: For sales and relationship management
- Marketing Automation: For campaign management
- Customer Service Platforms: For support ticket management
- E-commerce Platforms: For online sales
- ERP Systems: For operations and finance
- Analytics Tools: For behavior tracking
- Communication Platforms: For internal and customer communication
Customer data exists in all these systems. Without proper integration, they create independent silos diverging over time. Sales has one address, support another, billing a third.
Poor integration manifests as:
- Data Inconsistency: Same information has different values across systems
- Duplication Across Systems: Same customer exists as separate records in multiple platforms
- Missing Context: Support can't see purchase history, sales can't see support tickets
- Manual Workarounds: Spreadsheets and duplicate entry bridge gaps, introducing errors
- Delayed Propagation: Even with integration, sync delays mean decisions on stale information
- Transformation Errors: As data moves between different data models, transformations introduce errors
Integration Best Practices
Effective integration requires:
Clear Data Ownership: For each element, one system is authoritative, with others syncing from that source.
Bidirectional Synchronization: Data flows both directions with clear conflict resolution logic.
Real-Time or Near-Real-Time Sync: The longer data sits before syncing, the more likely decisions on outdated information.
Field Mapping Standards: Careful mapping ensures data lands correctly, maintains appropriate formats, preserves meaning.
Error Handling: Integration failures detected, logged, alerted immediately with retry logic for temporary issues.
Data Validation: Validate before syncing to prevent error propagation. Invalid data during sync should be quarantined and flagged.
Solutions from SyncMatters
SyncMatters specializes in creating seamless integrations maintaining data quality across complex technology ecosystems. As certified Elite HubSpot partner with deep expertise across monday.com, Salesforce, and other platforms, SyncMatters brings both technical capability and strategic understanding to integration challenges.
Comprehensive Integration Services
Custom CRM and ERP Integrations: SyncMatters creates tailored integrations between CRM platforms and ERP systems, ensuring seamless data flow between sales, operations, and finance. Custom connections account for unique business processes, data models, and workflow requirements rather than forcing organizations into generic templates.
45+ Pre-Built Connectors: For common integration scenarios, ready-to-deploy connectors dramatically accelerate implementation. Pre-built integrations cover major business platforms and embody best practices from hundreds of implementations.
Bidirectional Data Synchronization: All integrations support two-way flow with sophisticated conflict resolution logic. When changes occur in multiple systems, clear rules determine which prevails, with audit trails documenting decisions.
Real-Time or Scheduled Sync: Choose synchronization frequency based on needs—real-time for critical frequently-changing data, scheduled batches for large volumes or less time-sensitive information.
Automated Workflow Creation: Beyond just moving data, SyncMatters integrations trigger cross-system workflows. When sales opportunities progress, inventory automatically reserves, customer success notifies, billing prepares—all without manual coordination.
Error Resolution and Monitoring: Comprehensive monitoring detects integration failures immediately. Automated alerts notify administrators, detailed logs enable troubleshooting, retry logic handles transient failures without data loss.
Data Transformation and Enrichment: As data moves between systems, integrations transform formats, enrich with additional information, apply business logic, validate against rules—ensuring data arrives in optimal form.
Scalable Architecture: SyncMatters designs integrations to handle growing data volumes and increasing complexity without performance degradation.
Breaking Down Data Silos
SyncMatters specializes in creating unified customer views across fragmented technology landscapes:
CRM-ERP Integration: Connecting sales and operations ensures sales teams see real-time inventory availability, order status, delivery schedules. Operations gains visibility into sales commitments and forecasts. Finance accesses complete customer interaction history for credit decisions.
Marketing-Sales Alignment: Integration between marketing automation and CRM ensures leads flow smoothly with complete context, campaign engagement informs sales outreach, sales feedback improves marketing targeting.
Service-Sales Coordination: Connecting customer service platforms with CRM gives support teams complete customer context while alerting sales to upsell opportunities, renewal risks, and expansion possibilities identified during support interactions.
E-Commerce Integration: Synchronizing online store data with CRM provides complete purchase history, browsing behavior, cart abandonment signals, and product preference information enabling personalized marketing and informed sales conversations.
Integration and Data Quality
SyncMatters integrations directly enhance data quality through:
Automated Data Enrichment: As records sync between systems, missing information automatically appends from authoritative sources.
Validation During Sync: Data validates as it moves. Invalid formats correct, missing required fields flag, anomalies detect before propagation.
Deduplication Across Systems: Integrations identify when new records in one system match existing records in another, preventing cross-system duplication.
Standardization Enforcement: Data formats standardize during integration—phone numbers, addresses, company names, dates convert to consistent formats regardless of source.
Completeness Improvement: Integration surfaces gaps by bringing together partial information from multiple systems, creating complete profiles.
Audit Trails: Complete history of data flow between systems enables understanding how current state was reached, troubleshooting discrepancies, demonstrating compliance.
Strategic Integration Planning
SyncMatters provides strategic guidance beyond technical execution:
Technology Ecosystem Assessment: Evaluating current systems, understanding data flows, identifying gaps and redundancies, recommending optimization opportunities.
Integration Roadmap Development: Prioritizing integrations based on business value, effort required, and dependencies. Not everything needs integration on day one—starting with high-value connections and expanding systematically is often most effective.
Data Governance Framework: Establishing clear policies for data ownership, synchronization frequency, conflict resolution, validation rules, and quality standards spanning entire technology ecosystem.
Change Management Support: Helping organizations communicate integration benefits, train teams on new capabilities, evolve processes to leverage integrated systems effectively.
Certified Expertise
As Elite HubSpot partner, SyncMatters brings exceptional depth in HubSpot integrations while maintaining strong capabilities across:
- monday.com: Custom integrations with monday's flexible platform
- Salesforce: Deep experience with Salesforce APIs, AppExchange, ecosystem
- Google Workspace: Integration with Gmail, Calendar, Drive, Sheets
- Microsoft 365: Connections to Outlook, Teams, OneDrive, Excel
- Shopify, WooCommerce, BigCommerce: E-commerce platform integration
- QuickBooks, Xero, NetSuite: Financial and ERP system connections
This breadth means SyncMatters designs integration strategies working across entire technology landscape rather than optimizing for single platform.
Integration as Quality Enabler
Well-designed integration transforms isolated systems into unified platforms where:
- Data exists in one authoritative place and syncs everywhere needed
- Quality improvements propagate automatically across all systems
- Comprehensive customer context enables better decisions and experiences
- Manual workarounds and duplicate entry eliminate
- Real-time information supports agile operations
Organizations treating integration as strategic priority create foundations where self-cleaning CRM systems truly excel.
Best Practices for Maintaining CRM Data Quality

Technology alone can't solve data quality challenges. Even sophisticated self-cleaning systems require organizational commitment, clear processes, and user adoption.
1. Establish Clear Data Governance
Define Ownership: For every data element, clearly assign responsibility. When everyone is responsible, no one is responsible.
Document Standards: Create and maintain documentation defining acceptable formats, required fields, validation rules, data entry procedures. Make easily accessible.
Create Governance Committee: Form cross-functional team representing sales, marketing, service, operations, IT to establish policies, resolve conflicts, prioritize improvements.
Regular Policy Review: Policies should evolve as business changes. Quarterly or semi-annual reviews ensure relevance and effectiveness.
2. Implement Validation at Point of Entry
Required Fields: Determine essential fields for each record type and make mandatory.
Format Validation: Enforce proper formats for emails, phone numbers, dates, currency, structured data.
Dropdown Standardization: Replace free-text with controlled vocabularies wherever possible.
Real-Time Verification: For critical fields like email addresses, validate in real-time during entry.
Progressive Requirements: Collect minimum required information initially, then progressively gather additional details as relationships develop.
3. Automate Wherever Possible
Eliminate Manual Data Entry: Integrate systems so data captured in one place automatically populates others.
Scheduled Automation: Set up automated processes for routine tasks—weekly duplicate detection, monthly enrichment, quarterly obsolescence checks.
Triggered Workflows: Create workflows activating based on conditions—missing critical information alerts owner, data not updated in six months triggers verification.
Batch Operations: Provide tools for bulk operations rather than requiring individual record review.
4. Make Data Quality Part of Daily Workflow
Embed Quality in Processes: Build into normal workflows rather than treating as separate activity.
Gamification: Some organizations successfully use leaderboards showing who maintains cleanest data, recognition for quality champions, competitions with prizes.
Positive Reinforcement: Celebrate successes rather than just penalizing failures.
Reduce Friction: Make doing the right thing easy. Streamlined interfaces, smart defaults, automation reduce friction and encourage compliance.
5. Provide Training and Support
Comprehensive Onboarding: New users receive thorough training on quality importance, standards, entry procedures, available tools.
Role-Specific Training: Different roles interact with data differently. Customize for sales, marketing, support, administrators.
Ongoing Education: Regular refreshers, tips, updates on new capabilities, sharing best practices keep quality top-of-mind.
Easy Access to Help: Users should know where to go with questions—comprehensive documentation, help desk support, designated quality champions.
6. Monitor and Measure Continuously
Define Key Metrics: Establish specific, measurable data quality indicators like completeness rate, duplicate rate, validity rate, accuracy rate, decay rate, enrichment coverage.
Regular Reporting: Distribute quality dashboards showing current metrics, trends over time, comparison to targets.
Trend Analysis: Look for patterns. Are certain sources consistently producing low-quality data? Do quality metrics degrade at certain times?
Investigate Anomalies: When metrics suddenly change, investigate root causes.
7. Conduct Regular Audits
Scheduled Reviews: Periodic human review is valuable even with automated quality management.
Sample Audits: Statistical sampling provides insights into overall quality while requiring manageable effort.
Post-Mortem Analysis: When major issues are discovered, conduct root cause analysis.
External Validation: Occasionally validate CRM data against external authoritative sources.
8. Address Root Causes, Not Just Symptoms
Process Problems: If same errors keep occurring, process improvement may be needed rather than just fixing individual instances.
System Gaps: If issues stem from system limitations, address the system rather than asking users to work around problems.
Training Deficiencies: Recurring errors might indicate inadequate training or unclear procedures.
Misaligned Incentives: If users are rewarded for speed but not accuracy, quality suffers. Ensure incentives align with quality goals.
9. Balance Automation and Human Judgment
Automated for Routine: Use automation for high-volume, straightforward tasks.
Human for Complex: Reserve human review for ambiguous cases requiring interpretation or having potential business implications.
Clear Escalation Paths: Define when automated systems should escalate to human review based on confidence levels, data importance, or complexity.
Learning Loops: When humans resolve complex cases, feed decisions back into automated systems so they learn.
10. Treat Data Quality as Continuous Improvement
Iterative Enhancement: Start with foundational practices, measure results, learn what works, progressively enhance.
Technology Evolution: Stay informed about new quality capabilities in CRM platform and ecosystem.
Process Refinement: Regularly review quality processes for effectiveness and efficiency.
Cultural Reinforcement: Data quality should become part of organizational culture—something everyone understands as important.
11. Secure Executive Sponsorship
Demonstrate Business Impact: Connect quality to outcomes executives care about—revenue growth, customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, risk reduction.
Regular Updates: Keep leadership informed about metrics, initiatives, successes, challenges.
Resource Allocation: Ensure adequate budget and resources for quality initiatives.
Policy Enforcement: Executive support is essential when policies require enforcement.
12. Plan for Scale
Design for Growth: Processes should scale as record counts grow, user counts increase, complexity expands.
System Capacity: Ensure CRM platforms and quality tools can handle anticipated growth without performance degradation.
Team Capability: Build or acquire expertise to manage increasingly sophisticated systems as organization matures.
Continuous Investment: Budget accordingly for ongoing tools, training, resources.
These practices combined with modern self-cleaning technology create sustainable quality becoming competitive advantage rather than perpetual problem.
Implementing a Self-Cleaning System
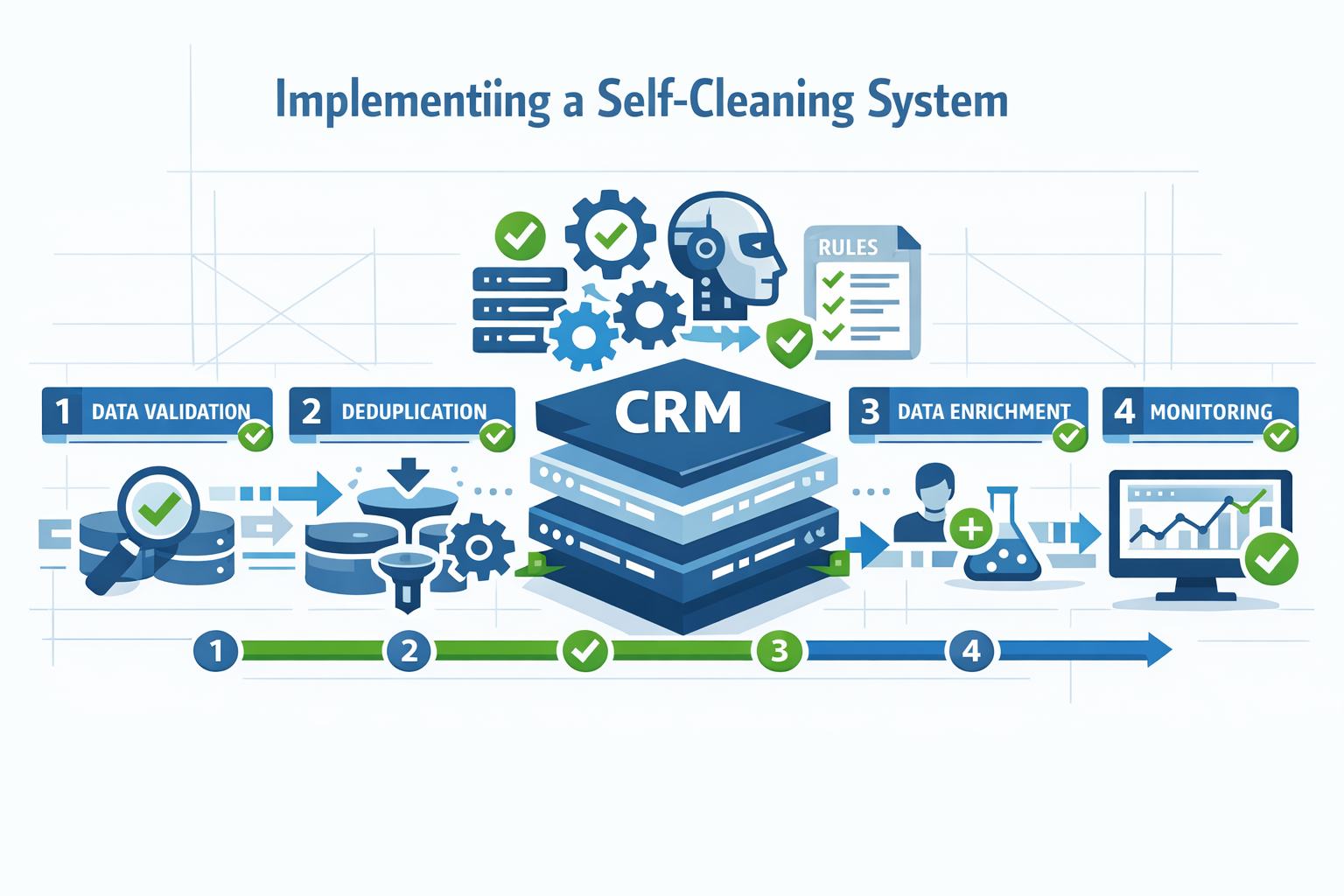
Transitioning from manual, periodic quality management to automated, continuous self-cleaning requires thoughtful planning and execution.
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (2-4 weeks)
Audit Current State: Analyze existing quality using metrics like completeness, accuracy, duplication rate, validity. Identify issues most impacting business. Evaluate current processes and tools. Calculate costs of poor quality.
Define Objectives: Establish specific, measurable goals (example: reduce duplicate rate from 15% to under 3%, increase completeness from 65% to 90%). Prioritize quality dimensions by business impact.
Evaluate Solutions: Assess self-cleaning capabilities of current CRM platform. Research third-party tools if native capabilities insufficient. Consider integration requirements. Evaluate build vs buy.
Plan Migration if Needed: If implementing self-cleaning requires CRM platform change, plan migration using services like MigrateMyCRM.
Secure Resources: Obtain executive sponsorship and budget approval. Assemble implementation team. Allocate time for stakeholders.
Phase 2: Foundation Building (4-8 weeks)
Establish Governance: Create data governance committee with clear charter. Document data standards. Define ownership. Establish conflict resolution policies.
Clean Existing Data: Deduplicate records using advanced matching. Standardize formats. Enrich incomplete records. Archive or delete obsolete data.
Configure Validation Rules: Set up required fields for each object type. Implement format validation. Create dropdown picklists. Configure cross-field validation. Set up duplicate prevention at entry.
Integrate Data Quality Tools: Connect to email validation services. Integrate with data enrichment providers. Set up automated deduplication. Configure address verification. Link to third-party platforms.
Phase 3: Automation Configuration (4-6 weeks)
Set Up Automated Workflows: Create scheduled processes for routine tasks. Configure triggered workflows activated by conditions. Establish automated escalation paths.
Configure Machine Learning: If platform supports ML-based duplicate detection, train initial models. Set confidence thresholds. Configure anomaly detection parameters.
Establish Data Enrichment: Configure automatic enrichment with publicly available data. Set up third-party provider integration. Define enrichment priorities. Establish refresh schedules.
Create Monitoring Dashboards: Build dashboards showing key metrics with historical trends. Set up alerts when metrics fall below thresholds. Create role-specific views. Establish regular reporting cadence.
Phase 4: Pilot and Refinement (4-8 weeks)
Limited Pilot: Start with one team, product line, or geographic region rather than full organization. Choose scope large enough to be meaningful but small enough to manage issues.
Monitor Closely: Track both quality metrics and user experience during pilot. Gather feedback on pain points, confusion, or unintended consequences. Measure efficiency gains.
Adjust and Optimize: Refine validation rules based on pilot experience. Adjust confidence thresholds for automated operations. Modify workflows based on user feedback. Update documentation.
Demonstrate Value: Share pilot results with broader organization. Highlight specific improvements. Collect testimonials from pilot participants.
Phase 5: Organization-Wide Rollout (8-12 weeks)
Phased Expansion: Roll out to additional teams progressively rather than flipping switch for entire organization overnight.
Comprehensive Training: Train all users on new validation rules, quality expectations, available tools. Provide role-specific training. Create easy-access help resources. Designate quality champions.
Communication Campaign: Explain why quality matters and how self-cleaning system benefits everyone. Share success stories. Set clear expectations. Maintain regular communication during rollout.
Support Intensive Period: Provide extra support capacity during initial weeks. Expect questions, confusion, adjustment challenges. Address issues quickly.
Phase 6: Optimization and Maturation (Ongoing)
Continuous Monitoring: Track quality metrics continuously. Watch for degradation. Analyze trends to identify opportunities for further improvement.
Regular Reviews: Quarterly review of metrics, policies, processes. Assess whether goals are being met. Identify areas for enhanced automation.
Expand Capabilities: As initial capabilities mature, progressively add advanced features. Implement more sophisticated ML models. Add additional data sources. Enhance integration.
Measure ROI: Track business impact of improved quality. Document time savings, revenue improvements, efficiency gains. Use ROI evidence to justify continued investment.
Cultural Reinforcement: Keep quality visible and valued through ongoing communication. Recognize and reward exceptional quality. Make quality part of performance expectations.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Expecting Overnight Transformation: Quality improvement takes time
- Insufficient Cleanup Before Automation: Clean the foundation first
- Overly Aggressive Automation: Don't auto-merge or auto-delete without adequate confidence
- Neglecting Change Management: Technology alone won't change behavior
- Inadequate Governance: Without clear ownership and accountability, initiatives drift
- Measuring Inputs Instead of Outcomes: Track business impact, not just technical metrics
- Treating It as Project Instead of Journey: Quality is an ongoing practice
Successful implementation balances technological capability with human factors—making systems effective while ensuring users understand, accept, and actively participate.
Measuring Data Quality Success
What gets measured gets managed. Establishing clear metrics enables tracking progress, demonstrating value, and identifying areas needing improvement.
Core Quality Metrics
Completeness Rate:
- Definition: Percentage of records with all required fields populated
- Calculation: (Records with complete required fields / Total records) × 100
- Target: 90%+ for critical fields, 75%+ for important optional fields
Duplicate Rate:
- Definition: Percentage of records that are duplicates
- Calculation: (Duplicate records / Total records) × 100
- Target: Less than 3% for mature systems
Validity Rate:
- Definition: Percentage of records where data in fields is valid/accurate
- Measurement: Email deliverability %, phone number validity %, address accuracy %
- Target: 95%+ for email addresses, 90%+ for phone numbers
Accuracy Rate:
- Definition: Percentage of records where data reflects current reality
- Measurement: Sample auditing against authoritative sources, verification of contact employment
- Target: 85%+ for B2B contact data (acknowledging ~20% annual decay)
Data Decay Rate:
- Definition: Percentage of records becoming outdated in given timeframe
- Target: Offset decay through continuous enrichment and validation
Enrichment Coverage:
- Definition: Percentage of records enhanced with third-party data
- Calculation: (Records with enriched data / Total records) × 100
- Target: 70%+ for B2B contacts and companies
Timeliness:
- Definition: How recently records were updated
- Measurement: Average days since last update, percentage updated in last 90 days
- Target: 80%+ of active records updated within 90 days
Business Impact Metrics
Sales Productivity:
- Time sales reps spend on data entry vs selling
- Number of contacts per representative can actively manage
- Percentage of calls reaching correct person
- Target: 20-30% reduction in administrative time
Marketing Efficiency:
- Email bounce rates
- Campaign delivery rates
- Cost per qualified lead
- Return on marketing investment
- Target: Bounce rates below 2%, 15-25% improvement in campaign performance
Forecast Accuracy:
- Variance between forecasted and actual results
- Confidence levels in pipeline projections
- Target: Reduce variance from typical 20-30% down to 10-15%
Customer Satisfaction:
- First-contact resolution rates
- Customer effort scores
- Net Promoter Scores
- Target: 10-20% improvement in satisfaction metrics
Revenue Impact:
- Deals influenced by data quality improvements
- Opportunities identified through enrichment that would have been missed
- Customer retention rates
- Target: 5-15% revenue improvement attributable to data quality
Operational Efficiency:
- Time spent on data quality tasks
- Cost of data quality maintenance
- Manual interventions required per month
- Target: 50-70% reduction in manual effort
Advanced Analytics
Data Quality Score: Composite score combining multiple dimensions weighted based on business priorities. Provides single number that's easy to track and communicate.
Source Quality Analysis: Track metrics by data source to identify which consistently produce high vs low quality data.
Quality by Record Type: Different record types may have different quality profiles. Understanding these patterns helps prioritize efforts.
Quality Trends Over Time: Are metrics improving, declining, or stable? Trending analysis reveals whether initiatives are working.
User Contribution Analysis: Which teams or individuals create highest quality data? Where are training or process improvements needed?
Reporting and Visualization
Executive Dashboard: High-level view of overall quality score and trends, business impact metrics, simple indicators, updated weekly or monthly.
Operations Dashboard: Detailed quality metrics across all dimensions, drill-down capability, real-time or near-real-time updates for day-to-day management.
Team Scorecards: Quality metrics specific to each team's records, comparison to organizational averages and targets for accountability and recognition.
Automated Alerts: Notifications when metrics fall below thresholds, early warning system for degrading quality enabling proactive intervention.
Using Metrics to Drive Improvement
Identify Priorities: Focus on quality dimensions with biggest business impact, address areas furthest from targets, pursue quick wins for momentum.
Root Cause Analysis: When metrics deteriorate, investigate why. Address underlying causes rather than symptoms.
Demonstrate Progress: Regular reporting shows improvements over time, celebrates successes, maintains momentum, justifies continued investment.
Continuous Optimization: Use metrics to identify automation opportunities, test improvements and measure impact, progressively raise standards as capabilities mature.
Measurement transforms data quality from vague aspiration to concrete, manageable objective.
The Future of CRM Data Management
The evolution of CRM data quality continues to accelerate. Understanding emerging trends helps organizations prepare and make strategic technology investments.
Predictive Data Quality
Current self-cleaning systems are largely reactive. Future systems will be increasingly predictive, identifying data likely to become problematic before quality degrades.
Predictive Decay Detection: ML models will analyze characteristics of records that tend to become outdated quickly, proactively flagging these for verification before they become inaccurate.
Proactive Enrichment: Rather than waiting for users to notice missing data, systems will predict which enrichment will be most valuable and automatically enrich before information is needed.
Quality Risk Scoring: Each record receives a quality risk score predicting likelihood of containing errors or becoming outdated, targeting high-risk records for extra validation.
Real-Time Data Quality
Instant Validation: All data validated in real-time as it enters systems from any source.
Continuous Enrichment: Records enriched continuously as new information becomes available.
Live Deduplication: Duplicate detection in real-time, preventing creation rather than identifying and merging after proliferation.
Streaming Data Quality: As systems operate on streaming data rather than stored records, quality processes will operate on data in motion.
AI-Driven Data Governance
Automated Policy Enforcement: AI systems will understand governance policies and automatically enforce them across all systems and users.
Intelligent Exception Handling: AI will make contextual decisions about appropriate handling when situations don't fit standard rules.
Dynamic Policy Adaptation: Governance policies will evolve based on changing business needs, with AI recommending policy updates when current rules prove inadequate.
Unified Customer Data Platforms
Single Source of Truth: CDPs create unified profiles that all systems access rather than customer data spread across separate systems.
Real-Time Synchronization: Changes propagate instantly across all integrated systems.
Comprehensive Quality Management: Quality processes operate on unified customer profile, ensuring quality maintained once centrally.
Advanced Identity Resolution: Recognize that interactions across channels, devices, touchpoints belong to same customer.
Privacy-Preserving Data Quality
Differential Privacy: Techniques enabling data analysis and quality assessment while preserving individual privacy.
Federated Learning: Quality models trained on decentralized data without transferring actual customer information.
Transparent Data Usage: Clear visibility into what data is collected, how it's used, who has access.
Automated Compliance: Quality processes automatically enforce privacy requirements.
Blockchain for Data Provenance
Immutable Audit Trails: Complete, tamper-proof history of all data changes.
Verified Data Sources: Cryptographic verification of data origins.
Decentralized Quality Verification: Multiple parties can verify quality without relying on single central authority.
Democratization of Data Quality
No-Code Quality Automation: Business users can create sophisticated workflows without programming skills.
Natural Language Interfaces: Query quality and configure rules using plain language.
Self-Service Quality Management: Teams manage quality for their domains without depending on centralized IT.
Hyper-Automation
End-to-End Process Automation: Complete workflows run without human intervention.
Self-Healing Systems: When issues are detected, systems determine root causes and implement fixes automatically.
Autonomous Optimization: Systems continuously test different strategies, measure effectiveness, automatically implement improvements.
Industry-Specific Quality Models
Healthcare: Quality models trained on medical data, understanding clinical workflows, ensuring HIPAA compliance.
Financial Services: Systems optimized for KYC requirements, fraud detection, regulatory reporting.
Manufacturing: Quality processes designed for complex supply chains, multi-tier customer relationships, product lifecycle management.
Retail: Solutions optimized for high-volume transactional data, seasonal patterns, omnichannel customer journeys.
The Path Forward
Organizations preparing for this future should:
- Build flexible foundations with open architectures
- Invest in AI capabilities and expertise
- Prioritize integration for unified customer data
- Develop data literacy across organization
- Stay informed about emerging capabilities
- Balance automation and oversight
The future is one of continuous, intelligent, automated management keeping pace with business speed. Organizations embracing this evolution create enduring competitive advantages.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between data cleaning and data quality?
Data cleaning is a specific tactical activity—identifying and correcting errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies in existing data. It's typically a periodic project to remediate accumulated problems.
Data quality is a comprehensive, strategic approach encompassing prevention (keeping bad data from entering), continuous maintenance (ongoing monitoring and correction), governance (policies and standards), and measurement (tracking quality metrics over time). Data quality includes cleaning as one component but extends far beyond it to create sustainable practices.
How much does poor CRM data quality actually cost?
The costs are both direct and indirect. Research shows companies lose an estimated 10% or more of annual revenue due to poor data quality. For a $10 million business, that's $1+ million annually.
Direct costs include: wasted marketing spend on undeliverable communications (often 20-30% of budget), sales time spent on dead leads and outdated contacts (17-23% of sales time), and customer service inefficiency from incomplete information.
Indirect costs include: poor strategic decisions based on inaccurate data, missed opportunities from overlooked leads, customer dissatisfaction from impersonal interactions, and compliance risks from data privacy violations.
Can I implement self-cleaning without changing my CRM platform?
Often yes, depending on your current platform and its capabilities. Many modern CRM systems include native self-cleaning features or support integration with third-party data quality tools. Solutions like Insycle, RingLead, Clearbit, and others integrate with multiple CRM platforms to provide automated quality management without platform migration.
However, if your current CRM is very outdated or lacks basic integration capabilities, you may get better long-term results from migrating to a modern platform with robust self-cleaning features. Services like MigrateMyCRM can make this transition straightforward while using migration as an opportunity to establish clean data foundations.
How long does it take to see results from self-cleaning implementation?
This varies by starting point and scope, but typical timelines are:
Quick Wins (2-4 weeks): Automated duplicate detection and basic validation show immediate improvements in data quality metrics and reduce user frustration with obvious errors.
Meaningful Impact (2-3 months): As enrichment runs, validation prevents bad data entry, and workflows automate quality tasks, teams notice significant time savings and improved data usability.
Transformational Results (6-12 months): Cultural shifts occur as data quality becomes normalized, trust in CRM increases, adoption improves, and business impact (revenue, efficiency, satisfaction) becomes clearly measurable.
The key is starting with high-impact use cases that demonstrate value quickly, then progressively expanding automation and sophistication.
What percentage of my data should I expect to be clean?
Benchmarks vary by industry and data type, but realistic targets for mature systems are:
- Completeness: 90%+ for critical fields, 75%+ for important optional fields
- Duplicates: Less than 3% of total records
- Email Validity: 95%+ deliverable
- Phone Validity: 90%+ valid format and potentially active
- Accuracy: 85%+ (recognizing that ~20% of B2B contact data decays annually through job changes and company evolution)
Perfection is unattainable—some amount of data will always be in flux, newly entered and not yet verified, or representing edge cases. The goal is minimizing quality issues to levels that don't significantly impact business operations.
Do self-cleaning systems eliminate the need for human involvement in data quality?
No—they dramatically reduce manual effort but don't eliminate human roles entirely. Humans remain essential for:
Governance: Establishing policies, standards, and business rules that automated systems enforce.
Exception Handling: Reviewing ambiguous cases where automated systems lack confidence to act autonomously.
Strategic Direction: Deciding which quality dimensions to prioritize, what investments to make, and how to balance automation with oversight.
Validation: Spot-checking automated decisions to ensure accuracy and providing feedback that improves machine learning models.
Complex Decisions: Handling unique situations that don't fit standard patterns and making judgment calls with business context.
Self-cleaning shifts human effort from routine data entry and correction to higher-value strategic data management and governance.
How do I get executive buy-in for data quality initiatives?
Connect data quality to business outcomes executives care about:
Revenue Impact: Demonstrate how poor data quality causes lost deals, reduces marketing ROI, and limits growth. Quantify the opportunity from improvement.
Operational Efficiency: Calculate time currently wasted on manual data quality work and project savings from automation.
Competitive Advantage: Show how superior customer data enables better experiences, more effective personalization, and faster response than competitors.
Risk Mitigation: Highlight compliance risks from poor data governance and potential regulatory penalties.
Strategic Enablement: Explain how clean data is prerequisite for other strategic initiatives—advanced analytics, AI implementation, customer experience transformation.
Use specific examples and case studies from similar organizations. Pilot programs that demonstrate results without requiring major upfront investment build confidence for broader initiatives.
What's the ROI timeline for self-cleaning CRM systems?
Most organizations see positive ROI within 6-18 months, though this depends on several factors:
Starting Point: Organizations with severely degraded data quality see faster ROI because improvements are dramatic. Those already managing quality reasonably well see more gradual gains.
Implementation Scope: Comprehensive implementations with full automation deliver greater long-term value but require more upfront investment. Focused pilots show faster ROI but smaller total impact.
Business Model: High-velocity sales environments with many customer interactions see ROI faster than slower-moving B2B contexts.
Typical ROI components include: reduced labor costs from automation (often 60%+ reduction in manual quality work), improved marketing efficiency (15-30% better campaign performance), increased sales productivity (20-30% time savings), and enhanced customer retention (5-15% improvement).
Can self-cleaning work with multiple CRM systems or a complex tech stack?
Yes, though it requires thoughtful integration strategy. Organizations operating multiple CRMs face additional complexity, but modern data quality platforms can operate across systems.
Key considerations:
Integration Architecture: Ensure data quality tools integrate with all platforms in your tech stack or use integration specialists like SyncMatters to create unified data quality processes.
Unified Governance: Establish consistent quality standards across all systems, even if implementation details vary by platform.
Master Data Management: Determine which system is authoritative for which data elements so quality improvements propagate correctly.
Cross-System Deduplication: Implement deduplication not just within individual systems but across your entire ecosystem to prevent the same customer existing separately in multiple platforms.
Complex environments require more sophisticated planning but can achieve excellent results with proper architecture.
How do I maintain data quality during rapid business growth?
Growth presents challenges but also opportunities:
Scale Through Automation: Manual data quality processes break down during growth, making automation essential rather than optional.
Build Quality into Onboarding: New users should learn data quality expectations from day one as part of standard onboarding.
Preventative Focus: As growth accelerates, preventing bad data becomes more important than cleaning it afterward. Emphasize validation at point of entry.
Monitor Metrics Closely: Watch for quality degradation as growth strains processes. Early detection enables intervention before issues compound.
Invest in Integration: As you add systems to support growth, ensure they integrate properly rather than creating new silos.
Scale Governance: Appoint data quality champions within growing teams to maintain standards without creating centralized bottlenecks.
Growth is the ideal time to establish strong data quality practices—it's easier to build good habits than to change bad ones later.
What should I do if users resist data quality requirements?
Resistance often stems from misunderstanding, misaligned incentives, or poor implementation. Address it through:
Communication: Explain how quality benefits users themselves—less time wasted on bad data, better results from campaigns, more accurate forecasts.
Reduce Friction: Make quality requirements easy to meet through automation, smart defaults, and streamlined processes.
Demonstrate Value: Show concrete examples of how clean data led to wins.
Adjust Incentives: Ensure compensation and recognition reward quality, not just quantity.
Address Real Concerns: Listen to resistance. Sometimes it reveals legitimate process problems or overly restrictive rules.
Executive Support: Visible leadership support makes clear that this isn't optional.
Start with Volunteers: Pilot with teams who are enthusiastic rather than forcing it on skeptics.
Change management is as important as technology.
How do privacy regulations like GDPR affect data quality management?
Privacy regulations actually make data quality more important, not less:
Accuracy Requirements: GDPR and similar regulations require maintaining accurate customer data and correcting errors when identified. Poor data quality violates these obligations.
Data Minimization: Regulations require collecting and retaining only data necessary for defined purposes. Quality processes help identify unnecessary data for deletion.
Right to Deletion: Honoring deletion requests requires finding all records associated with an individual—impossible with poor-quality, duplicated data scattered across systems.
Consent Management: Tracking what permissions customers have granted requires accurate, complete records linking consents to correct individuals.
Audit Requirements: Regulations often require demonstrating data governance practices. Automated quality processes create audit trails that manual practices can't match.
Modern self-cleaning systems often include compliance features—automated retention enforcement, consent tracking, audit logging—making regulatory compliance easier rather than harder.
Conclusion
The future of CRM data quality is clear: manual, periodic approaches are giving way to automated, continuous self-cleaning systems powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning. This transformation isn't just about better technology—it's about fundamentally rethinking how organizations approach customer data as a strategic asset.
The Imperative for Change
The traditional model of periodic database cleanups is unsustainable. Data decays at approximately 34% annually, meaning that no matter how thorough your cleanup project, significant degradation occurs within months. Meanwhile, businesses generate more customer data than ever, from more sources, at faster rates. Manual processes simply cannot keep pace.
Organizations continuing with periodic cleanups find themselves in perpetual cycles of degradation and remediation—never achieving sustained quality, always firefighting data problems instead of leveraging data as competitive advantage.
The Self-Cleaning Alternative
Modern self-cleaning CRM systems offer a fundamentally different paradigm:
Prevention Over Remediation: Stopping bad data from entering through real-time validation is more effective than cleaning it later.
Continuous Over Periodic: Ongoing automated monitoring and correction maintains quality rather than allowing degradation followed by cleanup.
Intelligent Over Rule-Based: Machine learning adapts to patterns, learns from corrections, and handles complexity that rigid rules cannot.
Scalable Over Labor-Intensive: Automation scales effortlessly with growing data volumes, users, and complexity where manual processes break down.
Proactive Over Reactive: Predictive systems identify likely quality issues before they materialize rather than only addressing problems after they occur.
Success Requires More Than Technology
While self-cleaning technology is powerful, successful implementations require:
Strong Foundations: Starting with clean data through expert migration services like MigrateMyCRM provides the baseline on which automation maintains excellence.
Comprehensive Integration: Unified data quality across the entire technology ecosystem through expert integration services like SyncMatters ensures quality is maintained everywhere customer data exists.
Clear Governance: Policies, standards, ownership, and accountability create frameworks that technology enforces.
User Adoption: Training, communication, and change management ensure teams understand quality importance and actively participate in maintaining it.
Continuous Improvement: Treating data quality as an ongoing journey rather than a destination, with progressive enhancement of capabilities and standards.
Executive Commitment: Leadership support for quality initiatives ensures adequate resources, policy enforcement, and organizational priority.
The Competitive Advantage
Organizations that achieve sustained high data quality create competitive advantages that compound over time:
Better Decisions: Strategy built on accurate, complete data yields superior results to decisions based on flawed assumptions.
Superior Customer Experiences: Personalization and responsiveness powered by clean data create experiences competitors with poor data simply cannot match.
Operational Excellence: Automation and efficiency enabled by reliable data reduce costs and free resources for strategic initiatives.
Faster Execution: Trust in data enables rapid decision-making and action where others must validate and verify before proceeding.
Sustainable Scale: Quality that maintains itself through automation enables growth without proportional increases in overhead.
Taking Action
The transformation to self-cleaning CRM systems is accessible to organizations of all sizes:
Small Businesses: Platforms like Zoho and Pipedrive provide powerful data quality capabilities at accessible price points.
Mid-Market Organizations: Solutions like monday.com combine sophisticated automation with user-friendly interfaces that don't require extensive technical expertise.
Enterprises: Platforms like Salesforce offer comprehensive ecosystems with deep AI capabilities and extensive third-party solutions.
Regardless of starting point, the path forward includes:
- Assess current data quality honestly and comprehensively
- Define clear objectives with measurable targets aligned to business outcomes
- Choose appropriate platforms that match your needs, budget, and technical capabilities
- Execute migration using expert services like MigrateMyCRM to establish clean foundations
- Implement integration with specialists like SyncMatters to unify quality across your technology ecosystem
- Configure automation progressively, starting with high-value use cases
- Train and communicate to build organizational understanding and adoption
- Measure and optimize continuously, treating quality as a journey not a destination
The Window of Opportunity
There's currently a strategic window for organizations that act decisively. While awareness of data quality importance is growing, most organizations still struggle with manual processes and periodic cleanups. Early adopters of self-cleaning systems establish advantages before these capabilities become standard.
Within the next few years, automated data quality will likely be as expected in CRM platforms as mobile access and cloud deployment are today. Organizations moving now gain first-mover advantages in customer understanding, operational efficiency, and strategic agility that late adopters will struggle to replicate.
Final Perspective
Customer data is the foundation on which modern business is built. Marketing campaigns, sales strategies, service experiences, product decisions, and strategic directions all depend on understanding customers deeply and accurately. Poor data quality undermines every initiative and limits every opportunity.
Self-cleaning CRM systems don't just solve a technical problem—they enable a fundamentally different relationship with customer data. Instead of viewing the CRM as a necessary evil requiring constant maintenance, organizations can rely on it as a trusted strategic asset that improves continuously and enables innovation.
The organizations thriving in 2025 and beyond will be those that treat data quality not as a periodic cleanup project but as a continuous, automated, strategic capability. The technology exists. The methodologies are proven. The business case is compelling.
The only question is whether your organization will lead this transformation or follow it. The time to act is now.
About the Solutions Referenced
SyncMatters is a leading provider of CRM integration and migration solutions, partnering with industry leaders including monday.com, HubSpot, and Salesforce. As a certified Elite HubSpot partner, SyncMatters specializes in strategic implementation, custom integrations, and data migration services that enable businesses to maximize their CRM investments. Their expertise spans custom CRM and ERP integrations, 45+ pre-built connectors, automated workflow creation, bidirectional data synchronization, and comprehensive data quality management across business systems. SyncMatters helps organizations break down data silos and create unified technology ecosystems where clean, consistent customer data flows seamlessly across all platforms. Learn more at syncmatters.com.
MigrateMyCRM (formerly Trujay) is a trusted CRM data migration platform with over 4,270 successful migrations completed. Supporting 25+ CRM systems and offering AI-powered automapping, unlimited free sample migrations, and enterprise-grade security, MigrateMyCRM makes transitioning to modern CRM platforms straightforward and secure. Their platform includes advanced features like duplicate prevention, custom field management, field usage analytics, complete relationship preservation, and flexible migration options from self-service to full-service implementations. ISO certified and GDPR compliant, they're trusted by organizations with the strictest security requirements. MigrateMyCRM transforms migration from a risky technical necessity into a strategic opportunity to establish exceptional data quality foundations. Learn more at migratemycrm.com.




